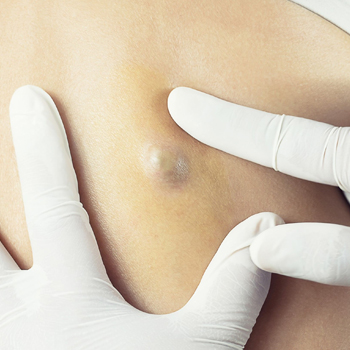
Sebaceous Cyst Excision
Sebaceous cyst excision is a surgical procedure to remove a sebaceous cyst, which is a non-cancerous, slow-growing lump beneath the skin. These cysts are typically filled with a thick, oily substance called sebum and develop when a sebaceous gland becomes blocked or damaged. Sebaceous cysts most commonly appear on the face, neck, scalp, or back, but they can occur anywhere on the body.
Reasons for Sebaceous Cyst Excision
- Cosmetic Concerns: When a cyst is visible and causes aesthetic discomfort, patients may seek removal for cosmetic reasons.
- Pain or Infection: If the cyst becomes inflamed, infected, or tender, surgical excision is often necessary to alleviate pain and prevent further complications.
- Recurrent Cysts: If a cyst keeps recurring despite draining or minor treatments, excision offers a more permanent solution.
- Risk of Rupture: In some cases, the cyst can rupture and cause discomfort or infection, making surgical removal necessary.
Procedure
- Consultation and Evaluation: A healthcare provider will examine the cyst to confirm it is benign (non-cancerous) and discuss the removal options with the patient.
- Anesthesia: The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia, which numbs the area to prevent pain during the excision. The patient remains awake during the procedure.
- Incision and Removal: A small incision is made over the cyst to access and remove the sac (or cyst wall) entirely. Removing the cyst wall is crucial to prevent the cyst from returning.
If the cyst has ruptured or is infected, additional cleaning may be required to remove any debris or pus. - Closure: The incision is typically closed with sutures, and a sterile dressing is applied to protect the area from infection.
Post-Procedure Care
- Wound Care: Patients are advised to keep the area clean and dry. The wound should be monitored for any signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or discharge.
- Pain Management: Pain is typically mild, and over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage discomfort.
- Follow-up: A follow-up visit may be required to ensure proper healing and remove any stitches after a few days, depending on the incision type.
- Scar Management: Scarring is minimal, but the area can be massaged and treated with silicone gel or sheets to help reduce scar formation.